SuperSocket Basic Configuration
Keywords: Basic Configuration, Configuration Documentation
A Sample Configuration
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<configuration>
<configSections>
<section name="superSocket"
type="SuperSocket.SocketEngine.Configuration.SocketServiceConfig, SuperSocket.SocketEngine" />
</configSections>
<appSettings>
<add key="ServiceName" value="SupperSocketService" />
</appSettings>
<superSocket>
<servers>
<server name="TelnetServerA"
serverTypeName="TelnetServer"
ip="Any"
port="2020">
</server>
<server name="TelnetServerB"
serverTypeName="TelnetServer"
ip="Any"
port="2021">
</server>
</servers>
<serverTypes>
<add name="TelnetServer"
type="SuperSocket.QuickStart.TelnetServer_StartByConfig.TelnetServer, SuperSocket.QuickStart.TelnetServer_StartByConfig"/>
</serverTypes>
</superSocket>
<startup>
<supportedRuntime version="v4.0" sku=".NETFramework,Version=v4.0" />
</startup>
</configuration>
Root Configuration
The configuration node "superSocket" is the root of the SuperSocket configuration, it defines the global parameters of SuperSocket requires. Let me explain all the attributes of the root node:
- maxWorkingThreads: maximum working threads count of .NET thread pool;
- minWorkingThreads: minimum working threads count of .NET thread pool;
- maxCompletionPortThreads: maximum completion threads count of .NET thread pool;
- minCompletionPortThreads: minimum completion threads count of .NET thread pool;
- disablePerformanceDataCollector: whether disable performance data collector;
- performanceDataCollectInterval: performance data collecting interval (in seconds, default value: 60);
-
isolation: SuperSocket instances isolation level
- None - no isolation
- AppDomain - server instances will be isolated by AppDomains
- Process - server instances will be isolated by processes
- logFactory: the name of default logFactory, all log factories are defined in the child node "logFactories" which will be introduced in following documentation;
- defaultCulture: default thread culture for the global application, only available in .Net 4.5;
Servers Configuration
In the root configuration node, there is child node named "servers", you can define one or many server configuration nodes in it which represent app server instances. The server instances can be same AppServer type, also can be different AppServer types. All server node's attributes:
- name: the name of the server instance;
- serverType: the full name the AppServer's type which you want to run;
- serverTypeName: the name of the selected server types, all server types should be defined in serverTypes node which will be introduced in following documentation;
- ip: the ip of the server instance listens. You can set an exact ip, you also can set the below values Any - all IPv4 address IPv6Any - all IPv6 address
- port: the port of the server instance listens;
- listenBacklog: the listen back log size;
- mode: the socket server's running mode, Tcp (default) or Udp;
- disabled: whether the server instance is disabled;
- startupOrder: the server instance start order, the bootstrap will start all server instances order by this value;
- sendTimeOut: sending data timeout;
- sendingQueueSize: the sending queue's maximum size, the default value is 5;
- maxConnectionNumber: maximum connection number the server instance allow to connect at the same time;
- receiveBufferSize: receiving buffer size;
- sendBufferSize: sending buffer size;
- syncSend: sending data in sync mode, default value: false;
- logCommand: whether log command execution record;
- logBasicSessionActivity: whether log the session's basic activities like connected and closed;
- clearIdleSession: true or false, whether clear idle sessions, default value is false;
- clearIdleSessionInterval: the clearing timeout idle session interval, default value is 120, in seconds;
- idleSessionTimeOut: The session timeout period; If the session's idle time exceeds the value, it will be closed in case of clearIdleSession is configured to be true; Default value is 300, in seconds;
- security: Empty, Tls, Ssl3. The security option of the socket server, default value is empty;
- maxRequestLength: The maximum allowed request length, default value is 1024;
- textEncoding: The default text encoding in the server instance, default value is ASCII;
- defaultCulture: default thread culture for this appserver instance, only available in .Net 4.5 and cannot be set if the isolation model is 'None';
- disableSessionSnapshot: Indicate whether disable session snapshot, default value is false.
- sessionSnapshotInterval: The interval of taking session snapshot, default value is 5, in seconds;
- keepAliveTime: The interval of keeping alive, default value is 600, in seconds;
- keepAliveInterval: The interval of retry after keep alive fail, default value is 60, in seconds;
-
certificate: it is a configuration element for X509Certificate which will be used in this server instance
there are two usage:
-
one is load certificate from cert file
<certificate filePath="localhost.pfx" password="supersocket" /> -
another one is load certificate from local certificate storage
<certificate storeName="My" storeLocation="LocalMachine" thumbprint="f42585bceed2cb049ef4a3c6d0ad572a6699f6f3"/>
-
-
connectionFilter: the name of the connection filter you want to use for this server instance, multiple filters should be delimited by ',' or ';'. Connection filters should be defined in a child nodes of root node which will be introduced in the following documentation;
-
commandLoader: the name of the command loader you want to use for this server instance, multiple loaders should be delimited by ',' or ';'. Command loaders should be defined in a child nodes of root node which will be introduced in the following documentation;
-
logFactory: the log factory you want to use for this server instance. If you don't set it, the log factory defined in root configuration will be used;
-
listeners: it is an configuration element which is designed for supporting multiple listening ip/port pair in one server instance. The listeners node should contains one or more child nodes of listener whose attributes defined like below:
ip: the listening ip; port: the listening port; backlog: the listening back log size; security: the security mode (None/Default/Tls/Ssl/...);for examples:
<server name="EchoServer" serverTypeName="EchoService"> <listeners> <add ip="Any" port="2012" /> <add ip="IPv6Any" port="2012" /> </listeners> </server> -
receiveFilterFactory: the name of the receive filter factory you want to use it for this server instance;
Server Types Configuration
Server types node is a collection configuration node under the root. You are able to add one/more elements with element name "add" and attributes "name" and "type":
<serverTypes>
<add name="TelnetServerType"
type="SuperSocket.QuickStart.TelnetServer_StartByConfig.TelnetServer, SuperSocket.QuickStart.TelnetServer_StartByConfig"/>
</serverTypes>
Because of the defined server type's name is "TelnetServerType", you can set the config attribute "serverTypeName" of the server instances you want to run as this type to be "TelnetServerType":
<server name="TelnetServerA"
serverTypeName="TelnetServerType"
ip="Any"
port="2020">
</server>
Log Factories Configuration
Same as server type configuration, you also can define one or more log factories and use it in server, the only one difference is the log factory also can be set in root configuration:
<logFactories>
<add name="ConsoleLogFactory"
type="SuperSocket.SocketBase.Logging.ConsoleLogFactory, SuperSocket.SocketBase" />
</logFactories>
Use it in root configuration:
<superSocket logFactory="ConsoleLogFactory">
...
...
</superSocket>
Use it in server node:
<server name="TelnetServerA"
logFactory="ConsoleLogFactory"
ip="Any"
port="2020">
</server>
Configuration Intellisense
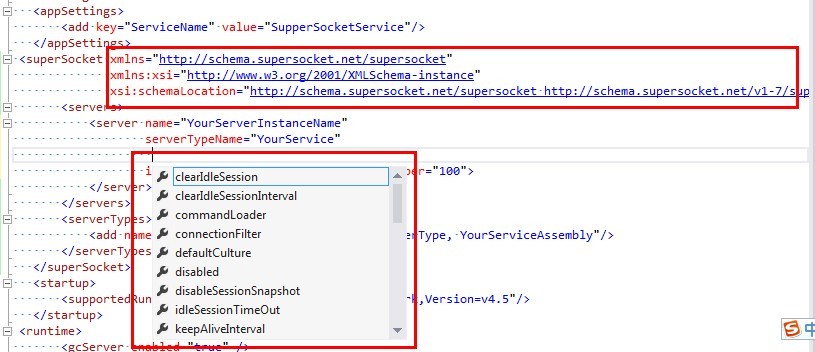
SuperSocket provides online XSD (XML Schema Document) file to help your configuration. You just need to add 3 extra lines in your SuperSocket configuration section:
<superSocket xmlns="http://schema.supersocket.net/supersocket"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://schema.supersocket.net/supersocket http://schema.supersocket.net/v1-6/supersocket.xsd">
<!---->
</superSocket>
Then you will get the intelligent auto completion function when you update the configuration:
SuperSocket Windows Service Configuration
As you know, SuperSocket provides a running container "SuperSocket.SocketService.exe" which can run as a windows service.
You can define the windows service's name by configuring:
<appSettings>
<add key="ServiceName" value="SuperSocketService" />
</appSettings>
There are some other configuration attributes for the windows service:
ServiceDescription: the description of this windows service
ServicesDependedOn: the other windows service which this service depends on; this windows service will start after the depended windows service; multiple depended service should be separated by character ',' or ';'